What is WebP? And how to use it
What is WebP?
WebP is a new image format developed by Google. WebP aims to deliver the same image file in a reduced file size. You may give your website's visitors the same experience by reducing the size of your image files, but your website will load faster.
According to Google’s WebP compression study , Google found that a WebP image file is on average:
- 25-34% smaller than a comparable JPEG image.
- 26% smaller than a comparable PNG image.
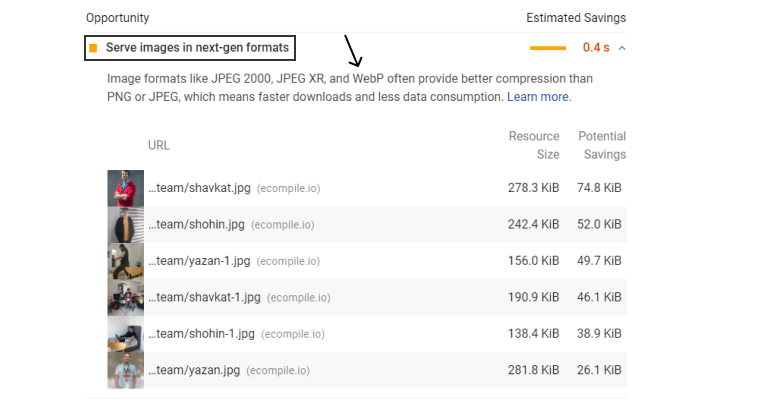
Even running your website through Google’s PageSpeed Insights , suggests to Serve images in next-gen formats, one of which is WebP:
Why is WebP better?
WebP supports both, lossy and lossless compression. Lossy means that the quality will be also degraded and the file size will be very small, while lossless reduces the file size by removing unnecessary metadata from your JPEG or PNG file. Below we can see the comparison between the two and JPG and PNG

As we can see from the image, WebP reduces the file size by almost 50%. While it might not make a lot difference when one is image is used, it will make a significant difference, if there are multiple images on your webpage.
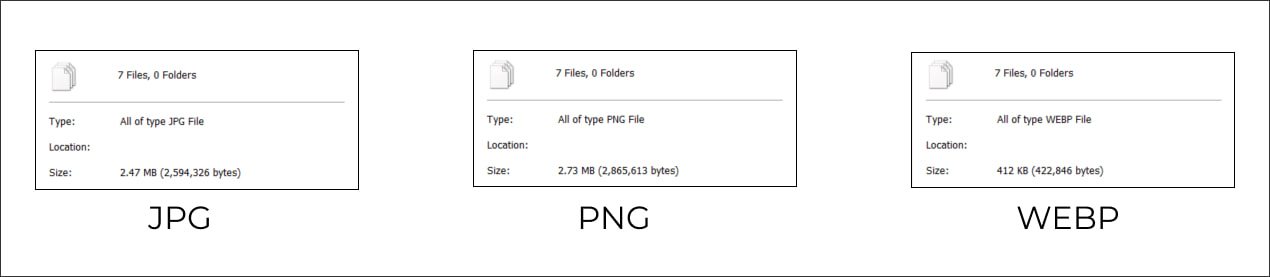
Our profile card images comparison
How to use WebP today?
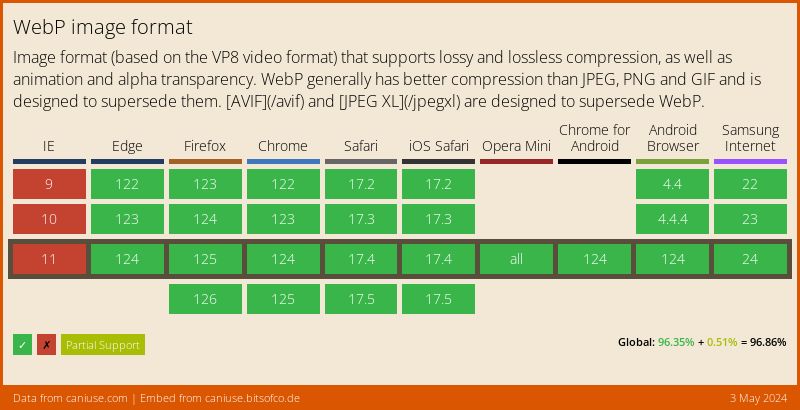
At the time of writing, WebP is supported in 95.64% of browsers globally used
Although it might seem like a good browser support, it isn’t the best to not provide a fallback image, as Safari (for both mobile and desktop) started the support of WebP images in 2020 only, with the release of MacOS Big Sur and iOS 14. It’s important to check what percentage of your website visitors are using a WebP supported browser. It should help you better decide whether to convert your images to WebP and how to serve a fallback images, as IE does not support picture element, which is so easy to use.
Example with fallback
Example for background image CSS
As for using WebP images for background, it is a bit trickier than and requires additional tools, such as Modernizr, which allows to detect if the browsers supports WebP, and adds the necessary classes to the html element.